Our Services
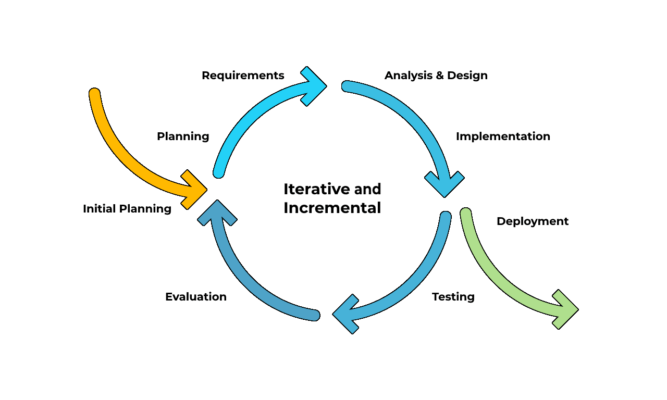
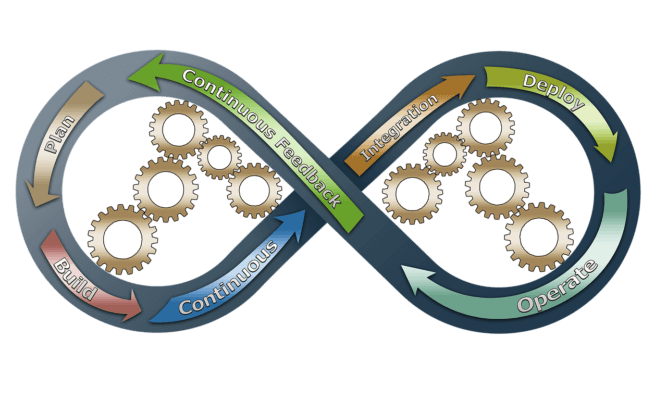
Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice of merging all developers’ working copies of a software several times a day to a shared source-code version control repository where automated tests can run.
The idea beneath CI is to provide rapid feedback so that if a defect is introduced into the code base, it can be identified and corrected as soon as possible. CI succeeded as a best practice because developers often tend to work in isolation waiting days or weeks to integrate their code. When they finally try to integrate their changes with the rest of the team’s code base many merge conflicts and hard to fix bugs arise. To avoid these problems CI requires the development team’s code to be merged to a shared version control branch continuously. The software produced from CI are then fed to release processes to drive frequent deployments.
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time and, when releasing the software, doing so manually.
The starting point for implementing CI and CD for your application development environment is to have the source code in a centralized version control system. Once you have configured CI, every time you push a change to your version control repository it will be automatically built and validated.
Benefits of CI / CD include:
- Increased speed of innovation
- Tested code is in production making money
- Smaller Code Changes
- Faster Release Rate
- Fault Isolations
- Increased Tests Reliability
- Smaller Backlog of Problems
- Increased Team Transparency and Accountability
- Reduced Costs
- Easy Maintenance and Updates
- Customer Satisfaction
Companies with more automation deploy faster. They understand the importance of CI/CD and set the pace of innovation for everyone else, specially their competitors.
Accuratica can help you increase agility, shorten releases, improve reliability and stay ahead of the competition with the use of Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery.